Chances and Challenges of Computational Approaches in the Humanities
From the Perspective of a Historical Linguist
Overview
- Introduction
- Background
- Chances of the New Approaches
- Challenges of New Approaches
- Computer-Assisted Frameworks
- Outlook
Introduction

Introduction
About me
- juggler since my youth (started juggling in 1992, since then trying to perform at least once a year on stage)
- historical linguist by training (2003-2008: magister studies in Sinology, Russian philology, and comparative-historical linguistics)
- computational experience acquired during doctoral studies (2009-2012: "Sequence comparison in historical linguistics")
- since 2012 working intensively on computer-assisted frameworks (experimenting with visualizations, JavaScript, and other frameworks for interactice applications)
Introduction
About my Work
- since my PhD studies, I work in data-driven, empirical frameworks
- apart from computer-solutions for basic tasks in historical linguistics, I am specifically interested in
- history of science in general and history of linguistics in specific
- philosophy of science
- the importance of linguistics and specifically historical linguistics outside of academia
Introduction
About my Project
- funded by the European Research Council (2017-2022)
- two post-docs, two doctoral students
- focus on computer-assisted language comparison
- special focus on Sino-Tibetan languages
- special interest: test the framework on more language families, but always in close contact with experts in the area (never work alone)
Introduction
About my Department
- Max Planck Institute for the Science of Human History, Jena
- Department of Linguistic and Cultural Evolution
- Strong focus on historical comparative linguistics (in contrast to the predecessor in Leipzig, mainly focusing on language typology)
Prologus

Prologus

Prologus
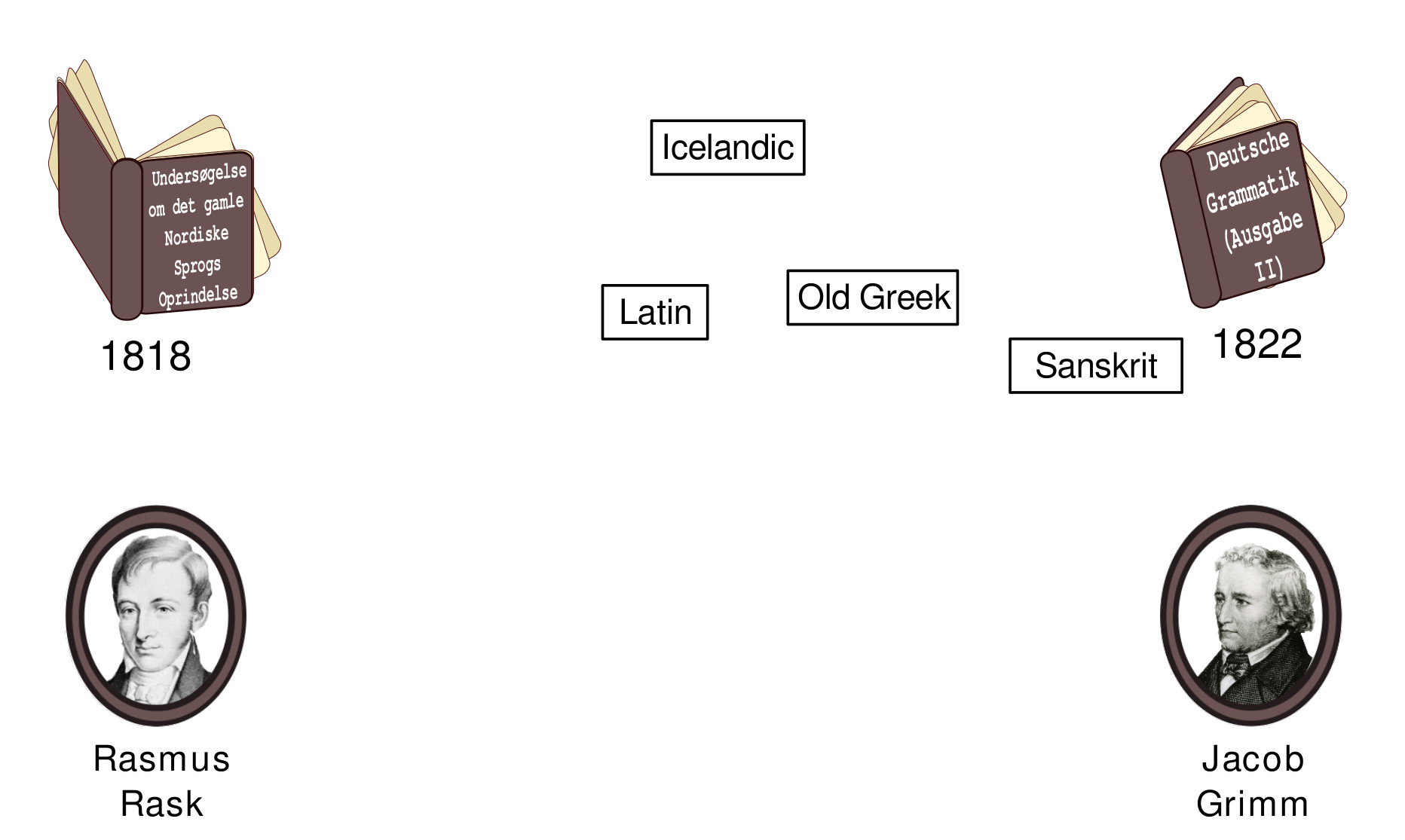
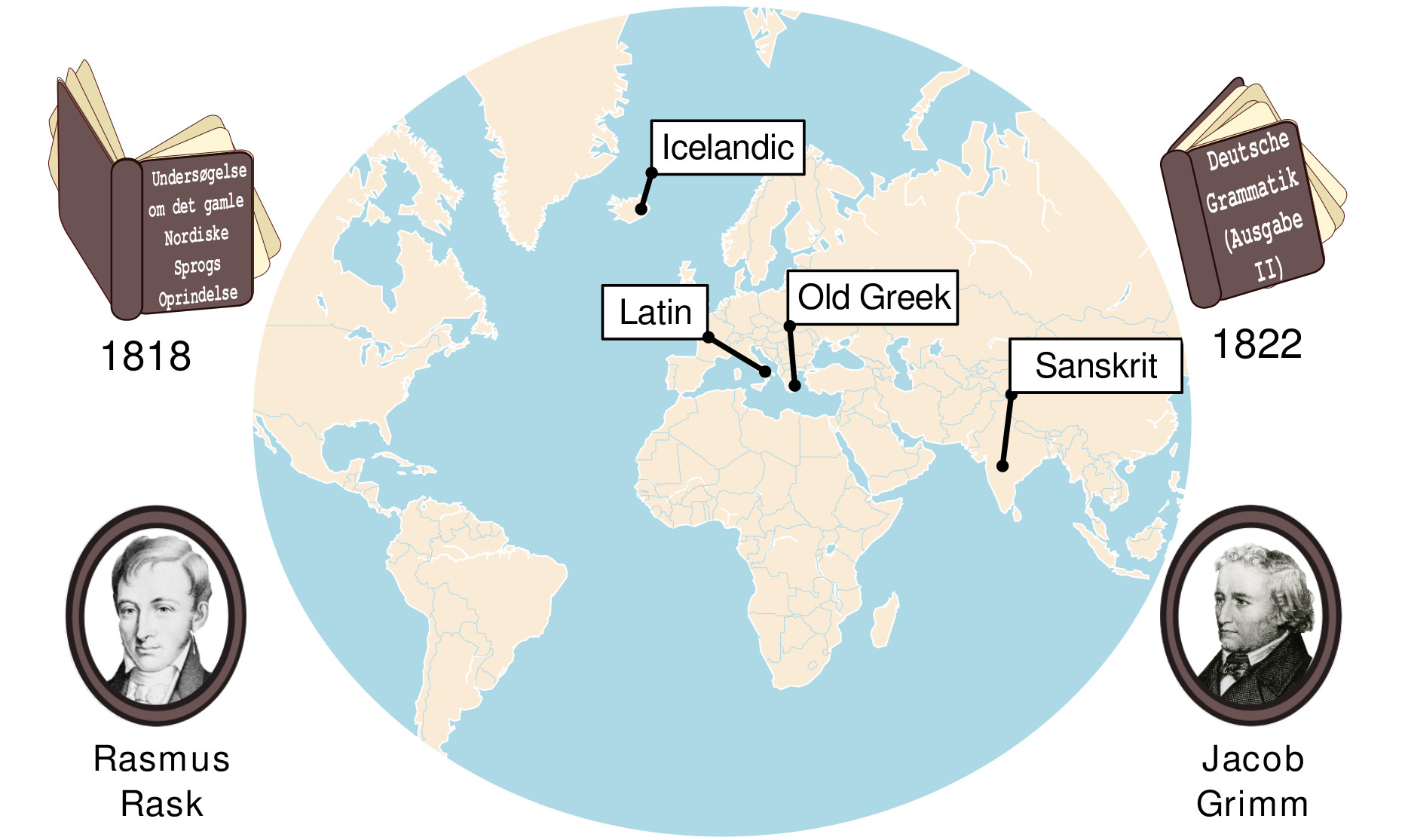
Classical Historical Linguistics
Prologus
Classical Historical Linguistics
Prologus
Classical Historical Linguistics

Prologus
Classical Historical Linguistics
Prologus
Classical Historical Linguistics

Prologus
Classical Historical Linguistics

Prologus
Classical Historical Linguistics
Prologus
Computational Historical Linguistics
Prologus
Computational Historical Linguistics

Prologus
Computational Historical Linguistics

Prologus
The Quantitative Turn

Prologus
The Quantitative Turn

Prologus
The Quantitative Turn

Prologus
The Quantitative Turn





Prologus
Promises of the new Methods
- increased consistency
- increased efficiency (faster analyses)
- new insights into the past of our languages
Chances of the New Approaches

Chances of the New Approaches
Automatic Cognate Detection

Chances of the New Approaches
Automatic Cognate Detection

Chances of the New Approaches
Automatic Cognate Detection
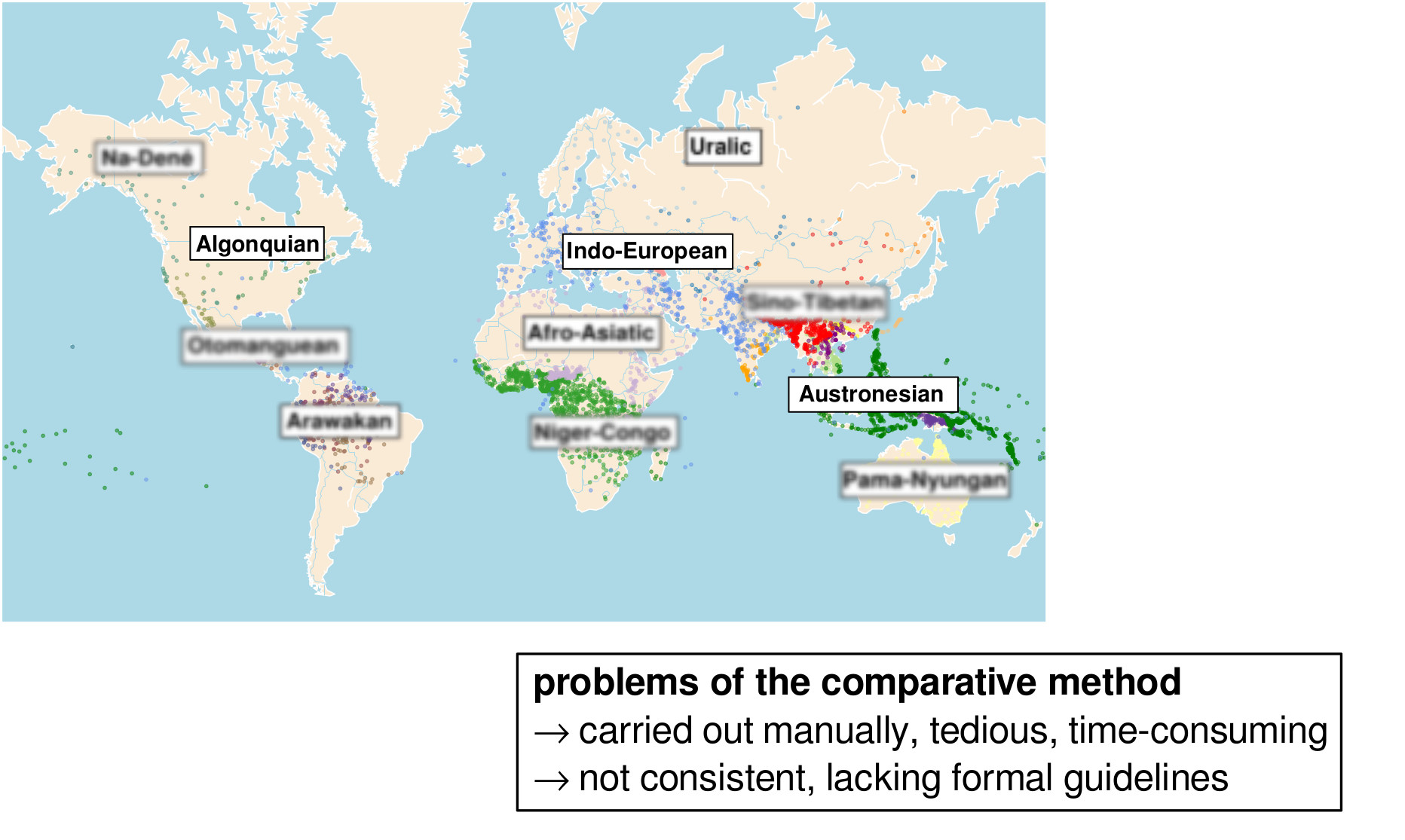
- detecting, which words across different languages go back to the same ancestor form (i.e., detect etymologically related words) is notoriously difficult and tedious
- the traditional method relies on an intensive comparison of words across different languages, during which patterns of regularly recurring sound correspondences are extracted and evaluated
- the result of this endeavour are the well-known etymological dictionaries which tell us where the words in our languages come from
Chances of the New Approaches
Automatic Cognate Detection
- etymologies play an important role in science, as far as they can help us to get insights into the history of our languages, but also in literature studies, in text criticism, and in the decipherment of ancient texts
- etymologies are also important in rhetorics, and in literature in practice, as they may inspire authors and speech writers in their literary "action"
- for a long time, the task of identifying etymologically related words automatically was considered to be impossible to be carried out by automatic approaches
Chances of the New Approaches
Automatic Cognate Detection
- starting with the pioneering work by Kondrak (2000), the task of automatic cognate detection was taken more seriously by different scholars with different backgrounds (computer science, computational linguistics, and classical historical linguistics)
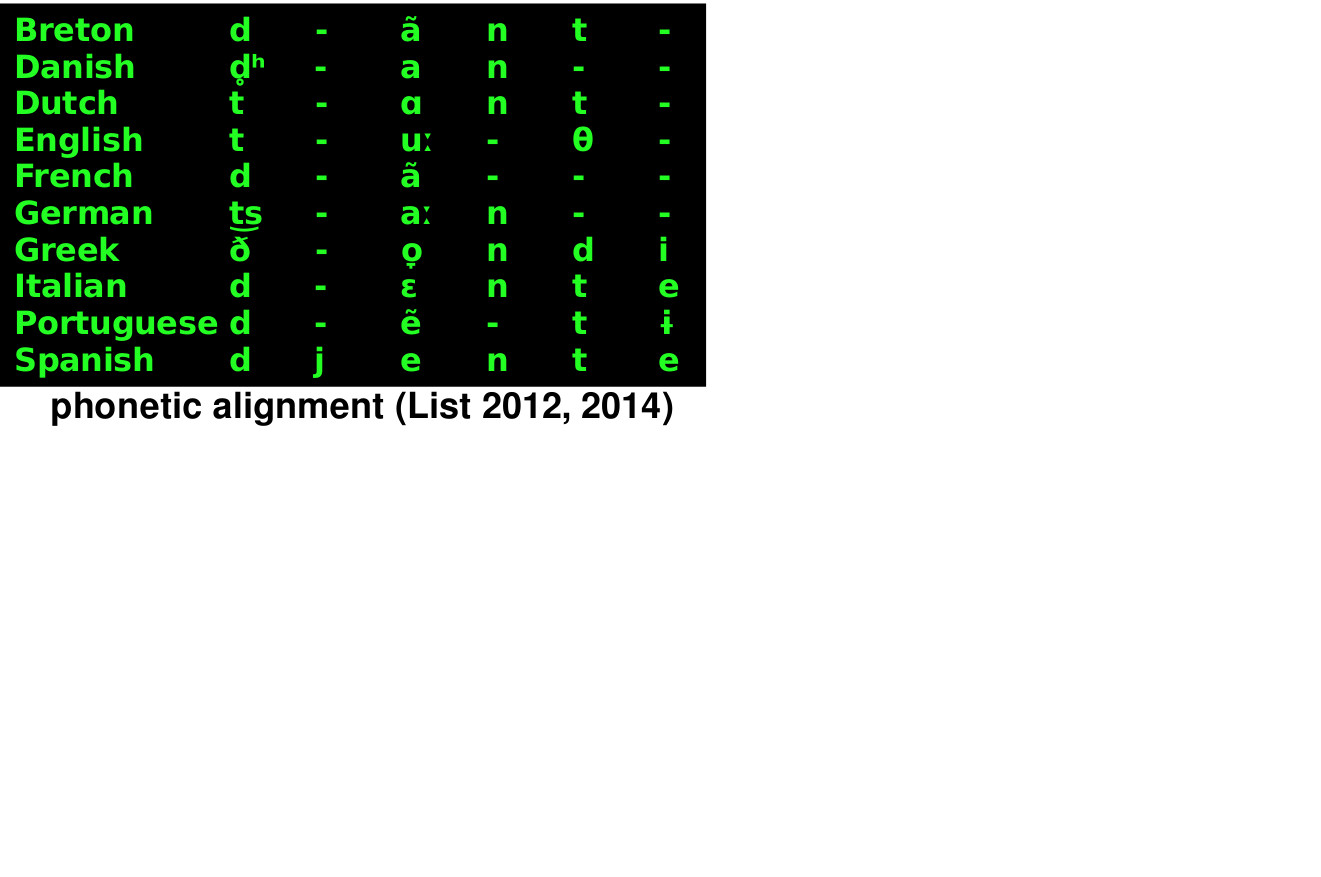
- based on new algorithms for sequence alignment, a method common in bioinformatics, that was considerably adopted to the needs of historical linguistics, List (2014) presented a stable Python library along with new algorithms that mimick the classical comparative method very closely
- a study by List et al. (2017) that further improved the algorithms reports average accuracy scores of 89% for tests on five different languages families
Chances of the New Approaches
Automatic Cognate Detection
LingPy:
- Python library for quantitative tasks in historical linguistics
- offers many methods for sequence comparison (phonetic alignment, cognate detection), phylogenetic reconstruction, ancestral state reconstruction, etc.
- collaborative work by a core team of currently two developers and many contributors in the past
Chances of the New Approaches
Automatic Cognate Detection: Partial Cognates

Chances of the New Approaches
Automatic Cognate Detection: Performance
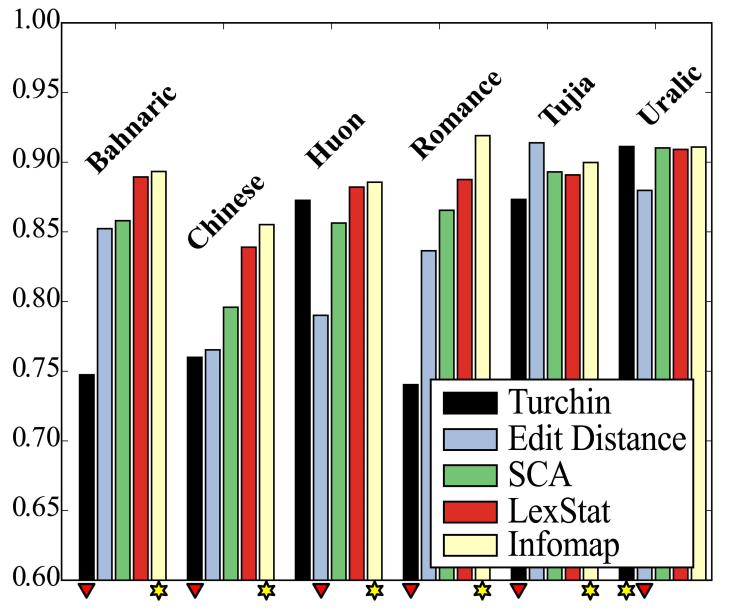
List, Greenhill, and Gray, PLOS ONE, 2017
Chances of the New Approaches
Automatic Cognate Detection: Performance
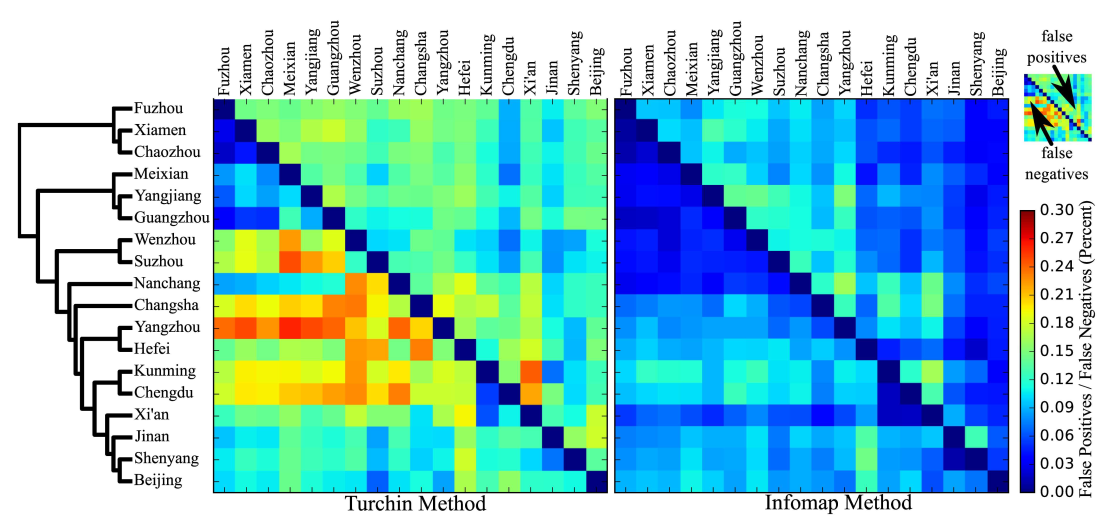
List, Greenhill, and Gray, PLOS ONE, 2017
Chances of the New Approaches
Automatic Cognate Detection: Performance
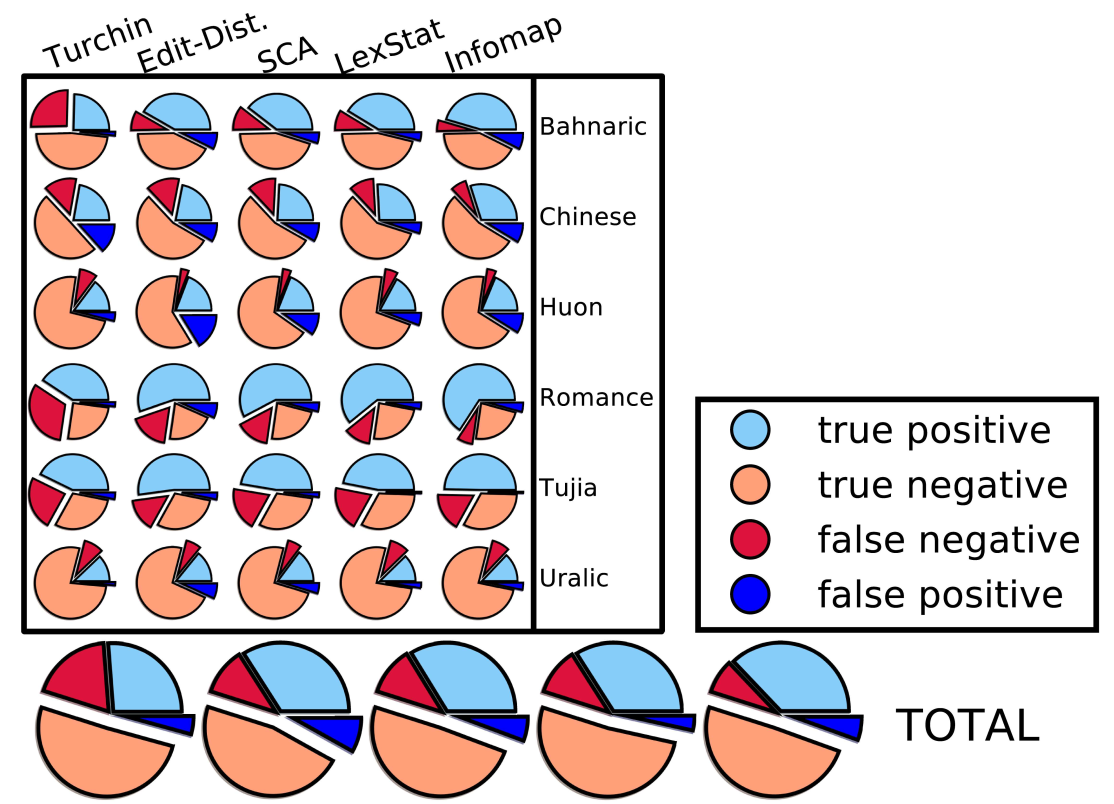
List, Greenhill, and Gray, PLOS ONE, 2017
Chances of the New Approaches
Automatic Cognate Detection: Summary
- although our algorithms will never be able to completely replace trained experts, they are good enough to assist experts, and they are usually better than untrained linguists, even if they know the languages they investigate very well
- the reason for the success of current methods for automatic cognate detection is a careful modeling of the classical method for cognate detection, which tried to take inspiration from similar tasks in evolutionary biology without blindly following the implementation that biology offers (adapt rather than transfer)
LINGPY.ORG
Chances of the New Approaches
Database of Cross-Linguistic Colexifications

Chances of the New Approaches
Polysemy, Homophony, Colexification
- Polysemy:
- If a word has two or more meanings which are historically related.
- Homophony:
- If two words which do not share a common etymological history have an identical pronunciation.
- Colexification (coined by François 2008):
- If one word form denotes several meanings.
Chances of the New Approaches
Colexification Networks
| Key | Concept | Russian | German | ... |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1.1 | world | mir, svet | Welt | ... |
| 1.21 | earth, land | zemlja | Erde, Land | ... |
| 1.212 | ground, soil | počva | Erde, Boden | ... |
| 1.420 | tree | derevo | Baum | ... |
| 1.430 | wood | derevo | Holz | ... |
Chances of the New Approaches
Colexification Networks
- concepts are represented as nodes in a colexification network.
- instances of colexification in the languages are represented as links between the nodes
- edge weights in the network reflect the number of attested instances of a given colexification or the number of languages or language families in which the colexification occured
Chances of the New Approaches
Analyzing Colexification Networks

Chances of the New Approaches
Analyzing Colexification Networks

Chances of the New Approaches
CLICS¹ Database
Database of Cross-Linguistic Colexifications (CLICS):
- CLICS¹ offered information on colexification in 221 different languages.
- 301,498 words covering 1,280 different concepts
- 45,667 cases of colexification, identified with help of a strictly automatic procedure, correspond to 16,239 different links between the 1,280 concepts in CLICS
Chances of the New Approaches
CLICS² Database
Problems of CLICS¹
- difficult to curate
- difficult to correct
- difficult to use computationally
- difficult to re-use by the community for similar projects
- difficult to expand (only three sources, only 221 languages)
Chances of the New Approaches
CLICS² Database
Basic ideas for CLICS²
- use standardized formats proposed by the Cross-Linguistic Data Formats initiative (Forkel et al. 2018) as basic format for representation
- link many different datasets to refernece catalogs like Concepticon and Glottolog
- make a new CLICS application with a transparent Python API
- separate data, data analysis, and data deployment
- create a CLLD (http://clld.org) application for easy deployment of the data
Chances of the New Approaches
CLICS² Database
Results for CLICS² (List et al. 2018)
- more than 1000 languages
- more than 1500 concepts
- full replicability with the clics2 Python API (https://github.com/clics/clics2)
- sources of CLICS² (15 different datasets) are fully traceable
- new web application more beautiful than before
- old "look-and-feel" is preserved thanks to a standalone application that runs on every server based on pure JavaScript
Chances of the New Approaches
CLICS Database
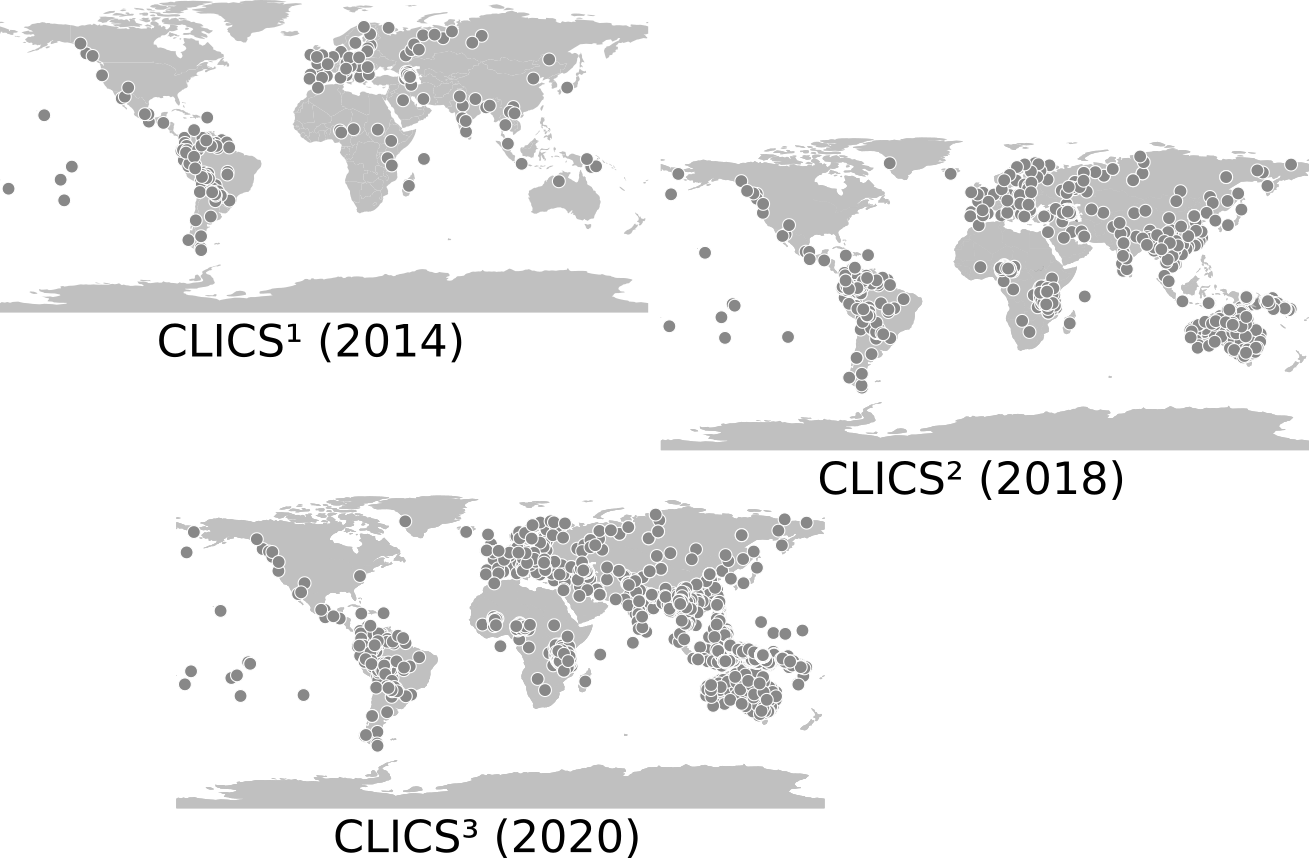
CLICS², Linguistic Typology, List et al. 2018
Chances of the New Approaches
CLICS Database

CLICS², Linguistic Typology, List et al. 2018
Chances of the New Approaches
CLICS Database

CLICS², Linguistic Typology, List et al. 2018
Chances of the New Approaches
CLICS Database

CLICS², Linguistic Typology, List et al. 2018
Chances of the New Approaches
Summary on CLICS
- CLICS provides information on patterns in the languages of the world that was not available in this form before
- CLICS uses a completely automatic workflow, but due to a thorough curation of the data as well as the direct presentation of the data with its sources to the experts, it makes it easy to spot potential errors quickly, while at the same time showing the major signal in the data which is rather unlikely to be affected by minor problems in the original data
- CLICS has the definite potential to provide us with new insights, while it also offers data in a form that could not be compiled by humans without technical support alone in a reasonable time frame
CLICS.CLLD.ORG
Chances of the New Approaches
Rhyme Networks in Ancient Chinese

Chances of the New Approaches
Rhyme Networks in Ancient Chinese

Chances of the New Approaches
Rhyme Networks in Ancient Chinese

Chances of the New Approaches
Rhyme Networks in Ancient Chinese

Chances of the New Approaches
Rhyme Networks in Ancient Chinese

Chances of the New Approaches
Rhyme Networks in Ancient Chinese
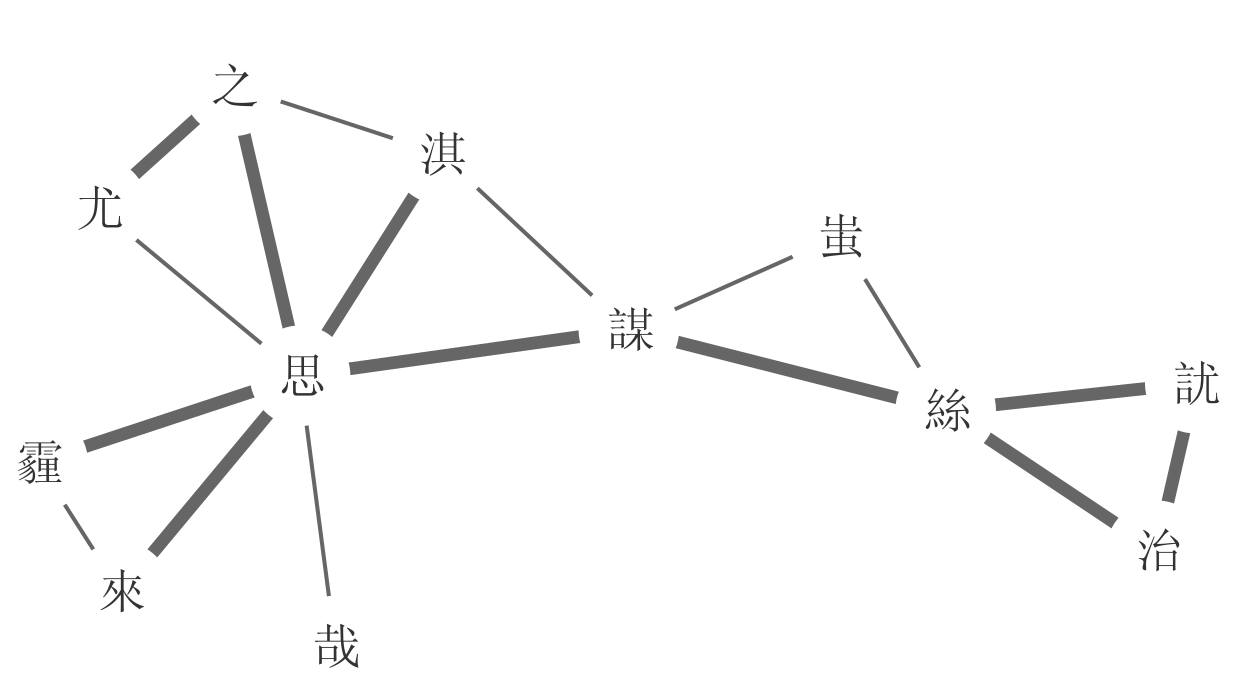
Chances of the New Approaches
Rhyme Networks in Ancient Chinese

Chances of the New Approaches
Rhyme Networks in Ancient Chinese

Chances of the New Approaches
Rhyme Networks in Ancient Chinese

Rhyme Networks, Bulletin of Chinese Linguistics, List 2017
Chances of the New Approaches
Rhyme Networks in Ancient Chinese

Rhyme Networks, Bulletin of Chinese Linguistics, List 2017
Chances of the New Approaches
Rhyme Networks in Ancient Chinese

Rhyme Networks, Bulletin of Chinese Linguistics, List 2017
Chances of the New Approaches
Rhyme Networks in Ancient Chinese

Rhyme Networks, Bulletin of Chinese Linguistics, List 2017
Chances of the New Approaches
Rhyme Networks in Ancient Chinese
- the rhyme network approaches (List 2017 and List et al. 2017) helped us to gain new insights into the structure of rhyme patterns in Chinese poetry
- thanks to the network representation of rhyme data, we could confirm and correct existing reconstructions of Old Chinese Phonology
- we could also illustrate that most reconstruction systems proposed for Old Chinese maintain a strict vowel purity, avoiding rhymes with different vowels
- the rhyme browser, that was created from the data, allows scholars quick access to the original data, so that they can spot errors, use it for their research, or correct it
DIGLING.ORG/SHIJING
Challenges of New Approaches

Challenges of New Approaches

Challenges of New Approaches
After the Quantitative Turn
Promises:
- increase in consistency
- increase in efficiency
- new insights
Challenges of New Approaches
After the Quantitative Turn
Reality:
- increase in consistency: on readily arranged data
- increase in efficiency: provided that data is readily arranged
- new insights: only regarding new questions
Challenges of New Approaches
After the Quantitative Turn
Benefits:
- data is taken seriously and people start thinking of how to provide it in a standardized form
- people start thinking how traditional problems can be tackled with new methods
- people ask new questions
Challenges of New Approaches
Data Problems
- many datasets that were used in the beginning of the quantitative turn were full of errors (Geisler and List 2010, and this lead to constant revisions, e.g., of Indo-European datasets, that were then still full of errors
- the core problem of the errors was that nobody initially really checked the data against the methods
- often, the data is even not made freely available with the papers, so checking data and code is even difficult for people who know how to apply the algorithms
Challenges of New Approaches
Data Problems
- journals often do not demand authors to publish data and code
- in my case, journals even retracted their invitation to review a paper because I was asking for data and code
- scholars are often also not very interested in checking the data submitted with papers, instead, it is quite common to criticize papers without even looking at the particular claims
- scholars conducting fieldwork in countries that welcome them and allow them to profit from their rich heritage in linguistic diversity often directly refuse to share their data "unless we have published some nice papers from them"
Challenges of New Approaches
Data Problems
- we need a paradigm change in the way we deal with data in historical linguistics (and humanities that go data-driven in general)
- not sharing one's data directly with a publication should be a no-go, and journals, scholars, and funding agencies should discourage such a behaviour
- when scholars are publicly funded, they should also be obliged to share their results, contrary to the current practice, where data rots in numerous computers, or is only provided in a form in which it is tedious if not impossible to reuse it for different kinds of research
Challenges of New Approaches
Data Problems: Suggestions
- standardize the data (compare our efforts in the CLDF initiative for linguistic data)
- make data human- and machine readable (teach scholars how to provide their data in a machine-readable form)
- propagate data sharing and re-use
Challenges of New Approaches
Data Problems: Work in our Group
- regular blogposts on issues related to data manipulation and curation (calc.hypotheses.org)
- a core team of developers who can all answer data-related questions and guarantee that we can help quickly when being contacted via email
- seminars, lectures, and tutorials in our in-house spring-school, at the university Jena, and different universities (upon invitation)
Challenges of New Approaches
Black Boxes and Dead Ends
Big Data Promise:
"with enough data, we can solve all problems, and we do not even know in detail, how the problems should be solved, as the machine learning algorithms will figure out which parameters work best on their own" (The Average NLP Representative I met in the Past)
Challenges of New Approaches
Black Boxes and Dead Ends
How Big Data and Machine Learning Works:
- create a dataset and measure different features (e.g., number of words in a text, number of bigrams, etc.)
- formulate the task as a decision question (e.g.: "is this a German text?", but not necessarily binary)
- feed the computer with annotated data in which the decisions are made by human experts
- use the trained model to solve more questions
Challenges of New Approaches
Black Boxes and Dead Ends
Problems of many machine learning frameworks:
- data is sparse in linguistics and humanities, but machine learning assumes that the data is big
- the features are poorly selected, without consulting experts and aiming for a careful modeling of what is already known to us
- results are a black box: they do not tell us how the internally selected features interact, or why a given output was produced after training the models
Challenges of New Approaches
Black Boxes and Dead Ends
Data sparseness:
- one million token corpora are nothing compared to what is used to have Google Translate provide at least approximately useful translations
- often, our linguistic data is restricted to wordlists of less than 500 words per language (but linguists can still squeeze out important signal from the data)
- our data is and never has been big in historical linguistics, but we have been able to develop methods to analyze the data anyway, yet our methods make use of more fine-grained models of the processes, which are lacking in machine learning approaches
Challenges of New Approaches
Black Boxes and Dead Ends
Feature design:
One of the promises of deep learning is that it vastly simplifies the feature-engineering process by allowing the model designer to specify a small set of core, basic, or “natural” features, and letting the trainable neural network architecture combine them into more meaningful higher-level features, or representations. However, one still needs to specify a suitable set of core features, and tie them to a suitable architecture. (Goldberg 2017: 18)
Challenges of New Approaches
Black Boxes and Dead Ends
Feature design:
- feature engineering or feature design (i.e.: modeling the processes we want to investigate) is largely ignored in most approaches
- scholars dream of a shortcut that allows them to infer something without going the hard way of figuring out how the processes actually work, or how a model can be created that approximates them in a useful way
- scholars at times criticize the use of "strong" models (as in our Python applications to cognate detection), since they are not "objective", but they misunderstand, that being objective does not require to be naive (t. b. c)
Challenges of New Approaches
Black Boxes and Dead Ends
The Black Box problem:
- since we do not know why trained models make the decisions they make, we have no way to learn from them (think of AlphaGo's success in Go: Go players now study the games by the machine to understand the strategies)
- since the models are trained on human annotations, the "objective" extraction of the most successful feature weights may as well reflect common human bias rather than scientific truth
- scientifically, a machine that tells us if two words are related or not is of no direct scientific value if we're interested in the deeper question of how we can prove word relatedness (it may be useful for other studies, but it does not solve scientific questions)
Challenges of New Approahces
Black Boxes and Dead Ends
The Black Box problem:

Lapuschkin et al. (2016)
Challenges of New Approaches
What are the Goals of our Research?
- What are the research questions in our field?
- What are the methods available to us to tackle these questions?
- Do our methods require data to be processed?
- Can we annotate the data efficiently?
Challenges of New Approaches
What are the Goals of our Research?
When quantitative approaches are useful:
- working manually on solving problems, you realize that they repeat boring tasks
- your research requires a larger collection of data to solve a problem
- the computational approach is promising to provide added value to your research, and especially: (1) you do not want to use computational methods only to make a fancy impression on colleagues and funding agencies, (2) you do not simply wish that some poor informaticion creates a fancy application for you
Computer-Assisted Frameworks

Computer-Assisted Frameworks
Computer-Assisted Language Comparison
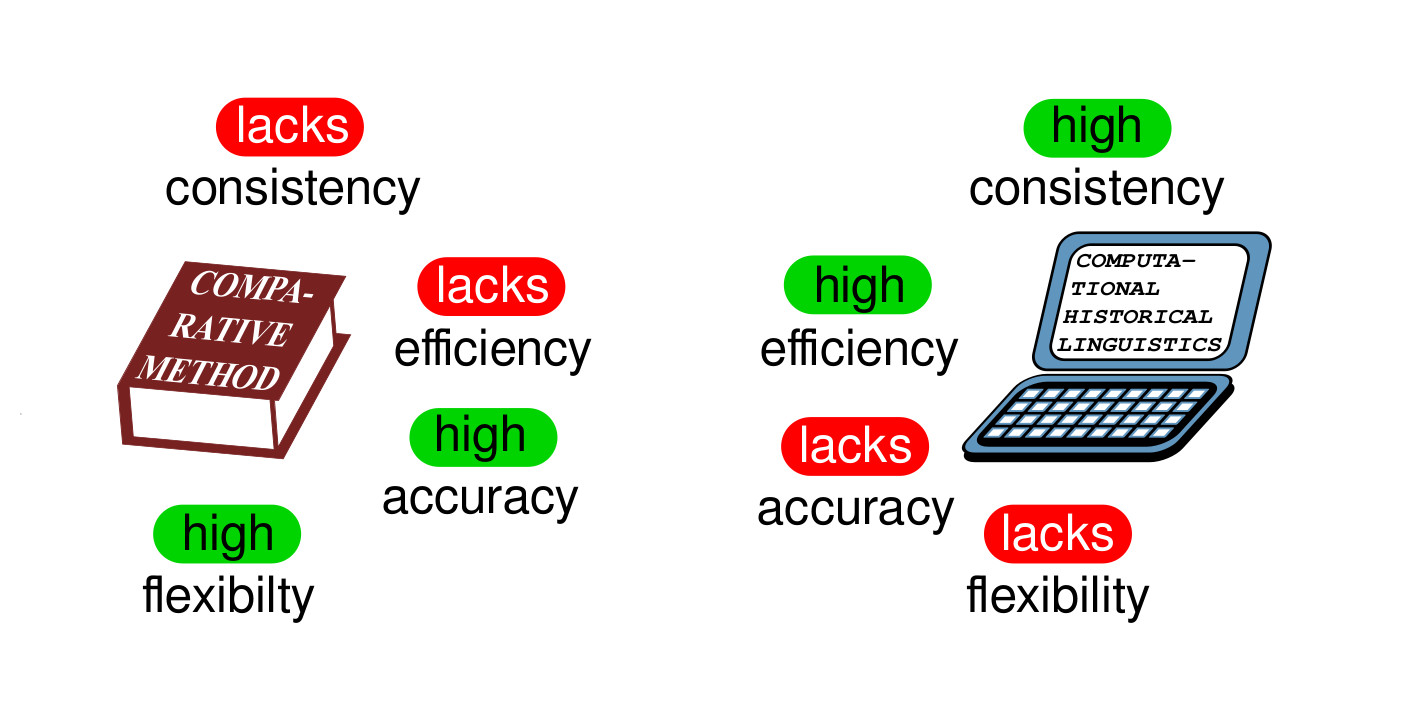
Computer-Assisted Frameworks
Computer-Assisted Language Comparison
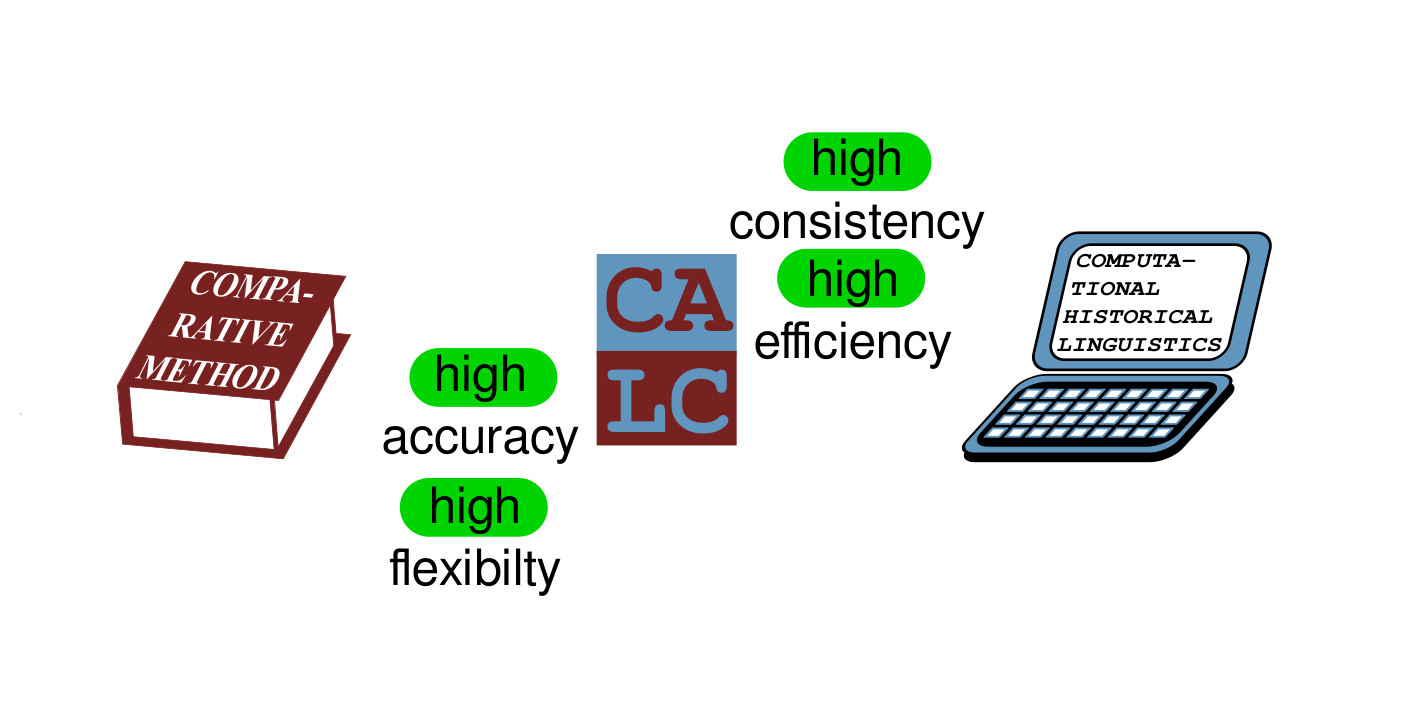
Computer-Assisted Frameworks
Computer-Assisted Language Comparison

Computer-Assisted Frameworks
Computer-Assisted Language Comparison

Computer-Assisted Frameworks
Computer-Assisted Language Comparison

Computer-Assisted Frameworks
Computer-Assisted Language Comparison

Cognate Detection and Annotation
Examples for CALC: Cognate Annotation
- The EDICTOR is a web-based tool that allows to edit, analyse, and publish etymological data.
- The tool can be accessed via the website at http://edictor.digling.org, or be downloaded and used in offline form.
- All that is needed to use the tool is a webbrowser (Firefox, Safari, Chrome).
- The tool can be used to annotate cognates and more relations in linguistic datasets.
- The major idea is to provide a framework for annotation in which data is always provided in human- and machine-readable form.
EDICTOR.DIGLING.ORG
Cognate Detection and Annotation
Summary on CALC
Benefits of Computer-Assisted Frameworks:
- get the best of the two worlds (efficiency of computers and flexibility of experts)
- embrace the power of annotation and modeling
- be realistic about (a) what can be done automatically, (b) what can't be done, and (c) what could be done (provided we improve our methods and models)
Outlook

Outlook
What can we learn from this for the humanities in general?
- rethink the big data vs. small data problem and the challenge for computer science
- foster a smart application of machine learning tools (no proof of concept but actual help for data-pre-processing in computer-assisted frameworks)
- improve computational training of scholars
- promote new scientific profiles (scholars who can bridge the gap and have training in classical and computational approaches)promote new scientific profiles (scholars who can bridge the gap and have training in classical and computational approaches)
¡Gracias a todos!
